The world is urbanizing at an unprecedented rate. By 2050, it is estimated that 66 percent of the global population will live in cities, up from 54 percent today. This migration to cities has led to the development of so-called “smart cities†– urban areas that use information and communication technologies to improve the quality of life for their residents.
Technological advances, including the internet of things (IoT), big data, and artificial intelligence (AI), make smart cities possible. These technologies allow cities to collect and analyze data from various sources, including traffic cameras, weather sensors, and social media. This data can be used to improve traffic flow, reduce pollution, and optimize energy use.
The definition of a smart city and its components
A smart city is a municipality that uses technology to improve the quality of life for its citizens. This includes using technology to make the city more efficient, reduce pollution, and make it easier for citizens to get around.
Some of the components of a smart city are:
Smart transportation: This includes smart traffic lights, which can adjust the timing of the lights based on traffic congestion, and smart parking, which can help drivers find parking spots.
Smart energy: This includes smart meters, which can help citizens track their energy usage, and smart grids, which can help utilities manage energy distribution.
Smart governance: This includes things like e-government, which allows citizens to conduct government business online, and smart policing, which uses technology to improve crime prevention and detection.
Smart buildings: This includes building automation, which uses sensors and controls to manage heating, cooling, and lighting, and smart waste management, which uses sensors to detect when a trash can is full and sends a notification to the sanitation department.
Smart living: This includes things like smart homes, which use technology to make it easier for citizens to manage their home environment, and smart healthcare, which uses technology to improve healthcare quality.
The history of smart cities and their origins
The term “smart city†is often used to describe a city that has been enhanced with information and communication technology (ICT) to improve its efficiency, sustainability and quality of life. While the origins of the smart city concept are difficult to trace, some several key events and movements have contributed to its development.
The first recorded use of the term “smart city†was in a 1998 report by the United Nations Centre for Human Settlements (UN-Habitat), which defined a smart city as “a city in which information and communication technologies are used to improve the quality and performance of urban services, to reduce the environmental impact of city operations, and to improve the quality of life of the city’s inhabitants.â€
The impact of smart cities on automotive research
The automotive industry is under pressure to innovate and develop new technologies to improve the driving experience, emissions and safety. Many of these new technologies are being developed in response to the needs of smart cities.
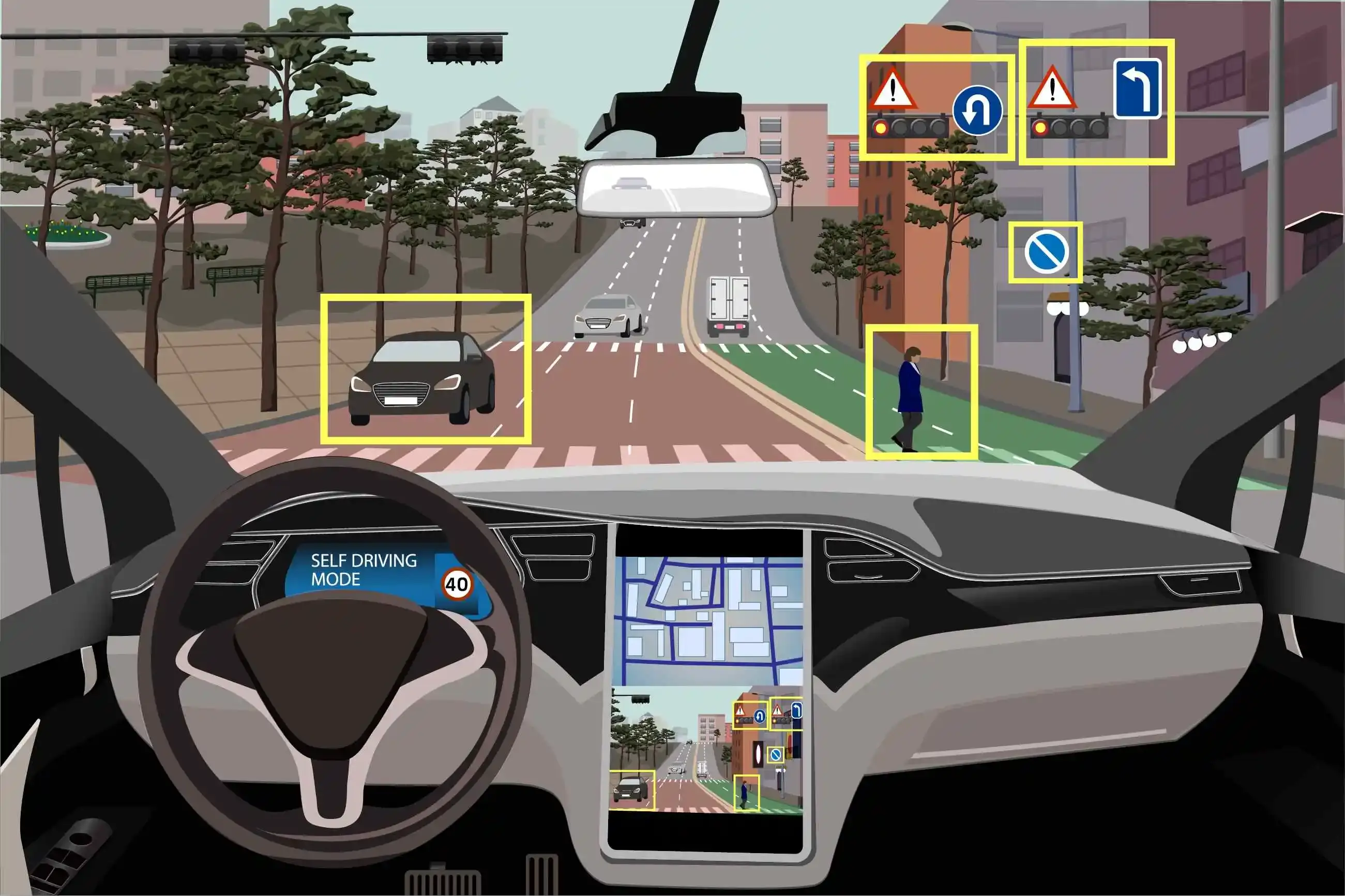
The rise of smart cities creates new opportunities for the automotive industry to develop technologies that improve the driving experience. For example, the need for improved traffic management and congestion relief is driving the development of new technologies such as autonomous vehicles and advanced traffic management systems.
The need for improved emissions and sustainability is also driving the development of new technologies. For example, the development of electric vehicles and alternative fuel sources.
The need for improved safety is also a major driver of automotive innovation. For example, the development of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles.
The benefits of smart cities for automotive research
1. Reduced traffic congestion and improved traffic flow: By monitoring and managing traffic flow through sensors and smart algorithms, traffic congestion can be reduced, leading to improved travel times and reduced emissions.
2. Improved parking availability and management: Smart parking solutions can help drivers find parking spots more quickly and efficiently and can also help manage parking congestion and pricing.
3. Enhanced safety and security: Smart city technologies can help improve safety for pedestrians, cyclists, and drivers through collision avoidance systems, smart lighting, and video surveillance.
4. Greater sustainability: Smart city solutions can help reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions through initiatives such as smart grid management, efficient transportation systems, and intelligent building management.
The future of smart cities and automotive research
In the near future, smart cities will rely on connected vehicles to manage traffic congestion, improve air quality, and optimize resources. By collecting and analyzing data from sensors embedded in roads, cars, and other transportation infrastructure, cities can make better decisions about managing traffic flow, parking, and public transportation.
The automotive industry is also investing in self-driving cars, eventually reducing traffic fatalities and improving safety. However, many challenges remain to overcome before self-driving cars become a reality. For example, how can we ensure that self-driving cars can handle all possible scenarios on the road? And how can we ensure they are compatible with the existing infrastructure?
These are just a few of the questions researchers are currently exploring in automotive engineering. By working together, the automotive industry and the smart city community can create a future where cars are not just a means of transportation but also a tool for improving the quality of life for all residents.
Conclusion
The rise of smart cities is transforming how we live, work, and move around in urban areas. Smart cities can use information and communication technologies to improve traffic flow, reduce pollution, enhance safety and security, and optimize energy use. The development of smart cities is also driving innovation in the automotive industry, with new technologies being developed to improve the driving experience, emissions, and safety.
The future of smart cities and automotive research is exciting, as cities will rely on connected vehicles to manage traffic flow and optimize resources. In contrast, the automotive industry will continue to invest in self-driving cars to reduce traffic fatalities and improve safety. By working together, the smart city community and the automotive industry can create a future where cars are not just a means of transportation but also a tool for improving the quality of life for all residents.





Comments (0)
Feb 17, 2023
Views (1474)